Calculation Method for Displacement-Dependent Earth Pressure on a Rigid Wall Rotating Around Its Base
کتابخانه الکترونیکی دیتا ساینس
شناسه: Article-2272021
عنوان: Calculation Method for Displacement-Dependent Earth Pressure on a Rigid Wall Rotating Around Its Base
لینک دانلود مستقیم:
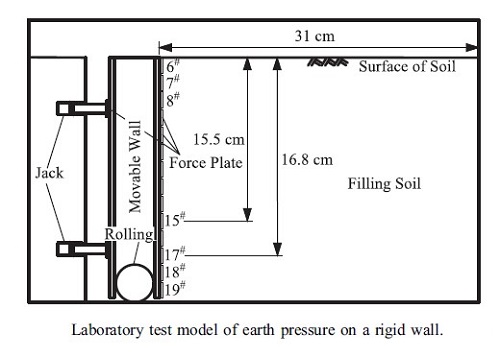
For the displacement-dependent earth pressure on a rigid wall that rotates around its base, an analysis approach will be established based on the Duncan–Chang stress–strain model, log-spiral potential slip surface in the retained soil, a horizontal slice method, and a graphical procedure to solve implicit expressions for the mobilized internal friction angle (φm) of the retained soil in the non-limit state. The shear strain on the potential log-spiral slip surface will be derived as a function of φm and height from the wall base. The active and passive ultimate wall displacements will be obtained based on the shear strain expression. A complete relationship between the earth pressure and wall displacement from the active to passive limit states of the soil will be quantitatively determined and calibrated by considering the practical wall displacement in the at rest state of the soil. Analysis results from examples indicate that the earth pressures by the proposed method are identical with those obtained via tests with a relative error of approximately 5%–10%. The profile of the earth pressure under the active and passive non-limit states are concave outward and inward to the wall, respectively. The two ultimate displacements decreased as the internal friction angle (φ) increased, and the active one decreased but the passive one remained almost unchanged with an increase in cohesion (c). In addition, the passive one increased slightly with the wall–soil friction angle (δ), but the angle did not influence the active one.